What is distributed storage?
Distributed storage is a software-defined storage system that enables access to data - when you want, where you want and whom you want to access. Distributed storage is a logical volume management system designed to process scale and data access in a HA (High Available) environment with intelligence to detect and respond to failures and cyber attacks. Replacing the traditional three-tier architecture with a distributed file system, it is made up of data stored on clusters of storage nodes that are geographically dispersed. The storage system includes features that synchronise and coordinate data across the cluster nodes.
What is distributed cloud storage?
Distributed cloud storage is a type of cloud storage architecture that extends the principles of distributed storage to the cloud computing environment. Distributed cloud storage is related to traditional cloud storage, but there’s one important difference. Instead of data stored on a collection of storage devices in one datacentre, distributed cloud storage is made up of data stored on clusters of storage nodes that are geographically dispersed. The storage system includes features that synchronise and coordinate data across cluster nodes, significantly simplifying storage rollouts and management. Since the data is distributed, you have the option to employ cloud-based data monitoring tools for identifying, preventing, recovering from, and analysing cyber attacks. Shared storage is a big target for ransomware attacks, but the data governance features of the distributed cloud storage greatly help to detect signatures, block user sessions, endpoints and perform forensic analysis, and aiding in recovery efforts following an attack.
The “distributed” nature of this type of cloud storage is important because it allows cloud data to be stored in closer proximity to an organisation’s physical location such as ROBOs (Remote Office & Branch Offices). It opens up new possibilities for location-dependent cloud use cases and can result in faster data transfers, reduced network congestion, and lower risk of data loss.
Based on edge computing and storage, distributed cloud storage represents the next step in cloud storage, one that puts data closer to where it’s needed. Public cloud providers such as AWS have long acknowledged the value in keeping data close to where it will be used, as evidenced by their multiple zones and region-based offerings.
How distributed storage works
Public cloud providers distributed their storage services across various physical locations, aiming to minimise latency by storing data in close proximity to its intended usage location.
Distributed cloud storage blurs or eliminates the lines between public, private, and hybrid clouds, allowing administrators to manage data across all three storage types through a unified control plane.
Why is distributed storage important?
- Software-defined - distributed storage replaces the traditional centralised SAN and NAS with a software-defined storage platform that empowers customers to deploy, manage, and scale a single, unified storage platform across datacentres, branch offices, or the cloud. An integrated distributed storage platform enables seamless access to storage by delivering files, objects and volumes across multiple protocols to all workloads and users.
- Access to all protocols - customers have been procuring Files, Objects and Volumes as point solutions and are managed by independent teams. A distributed storage system offers simplicity, consolidating all three access types on a single platform, helping customers to deploy the storage services at core/edge or to extend to the cloud. Additionally, all three storage services are managed and monitored centrally.
- Scale-out architecture - in contrast to traditional storage arrays, distributed storage is by design a scale-out architecture. You have the flexibility to add an unlimited number of nodes, thereby expanding the storage capacity indefinitely.
- Faster provisioning - since the distributed storage system creates a shared pool of storage resources from a number physical nodes, storage policies can be created and attached to virtual machines that can instantaneously leverage resources from the dynamic storage pools. This makes faster storage provisioning unlike traditional storage where an administrator has to create a volume/file share and attach to the virtual machine manually.
- Simplified management and monitoring - distributed storage system offers simple management and monitoring with dashboards, data analytics tools, etc.
Distributed storage features
While features can vary across cloud storage providers, most distributed cloud storage systems include:
- Partitioning – allows users to spread data across cluster nodes, facilitating easy access to the data from those nodes.
- Replication – data is copied across different nodes and ensures consistent updates whenever the data undergoes modification.
- Resiliency – ensures the continued availability of data, even in the event of malfunctions in one or multiple nodes.
- Easy scaling – system operators can scale storage capacity up or down as needed, simply by adding or removing nodes to the cluster.
Pros and cons of distributed cloud storage
Advantages:
- Aids regulatory compliance – many regulations restrict organisations from moving sensitive data across borders; now, they can more easily keep country data in-country, for example.
- More ambiguous attack surface – the absence of centralised servers makes it less predictable for attackers to identify a single target. With distributed storage spreading data among multiple nodes, it minimises the potential impact of an attack.
- Reduced risk of network failure – the decentralised nature of distributed storage enhances fault tolerance. If a portion of the network experiences failure, the rest of the system can continue to operate, ensuring ongoing data availability and mitigating the impact of network failures.
- Enhanced privacy – data fragmentation, encryption, access controls, and decentralisation reduce vulnerabilities. Dynamic resource allocation, geographic distribution, and redundancy features further contribute to increased privacy protection by dispersing and securing data across multiple nodes.
- Reduced energy costs – the efficiency of resource utilization is enhanced by the decentralised nature of this storage, as it eliminates the need for large centralised datacentres.
Disadvantages:
- Bandwidth – the inclusion of various cloud storage types and systems in distributed storage may lead to different connectivity models, putting strain on edge-located internet connections and causing bandwidth issues.
- Security – ensuring data security across diverse cloud storage types dispersed globally can be challenging, posing potential vulnerabilities and security risks.
- Data protection – backup and business continuity can get tricky, especially when it comes to making sure geography-limited data stays where it should.
Cloud computing vs distributed cloud: which is better?
The centralised, traditional cloud storage systems we have come to know and use are perfectly suitable for most organisations and are expected to persist. However, the likelihood is that distributed cloud storage will become increasingly popular, especially as edge computing and location-specific use cases proliferate.
While centralised cloud storage relies on a datacentre with numerous servers, distributed cloud storage disseminates data across its network to individual devices or computers. The primary advantage of this approach is enhanced reliability, as storing data on multiple storage servers builds resilience and safeguards against data loss.
Distributed cloud storage reduces latency by storing data in proximity to its intended usage location. In contrast, the traditional cloud model may incur significant latency as data travels across the country or the globe. Lower latency equals improved performance—and a better user experience overall. Distributed cloud storage also outperforms the centralised model because it is a greener solution and can help organisations save significantly on energy costs. There’s no need for enormous cooling systems—or even a datacentre building that requires light and heat.
Distributed cloud storage also enhances data security and data protection. A single instance of data can be split across multiple sites or multiple instances of data can be replicated across multiple sites. Both cases offer heightened data protection in case of DR events, Ransomware attacks, etc.
Edge computing vs distributed cloud
Edge computing is a distributed IT architecture where data is processed at the edge of the network, as close to the originating source as possible. This ideally puts compute and storage at the same point as the data source. While distributed cloud computing is a software system that is shared among multiple computers and runs as one system to improve efficiency and performance.
Examples of distributed cloud storage
Distributed cloud storage forms the foundation of some popular cloud storage systems, such as Amazon S3 and Microsoft Azure Blob Storage. Another good example of distributed cloud storage is a content delivery network (CDN), such as Netflix or YouTube. These companies store their video content in specific geographic locations around the world, nearer to where that content will be watched (think people watching a show in China versus someone accessing an English-language video in the UK). This helps reduce latency.
Distributed storage and Nutanix
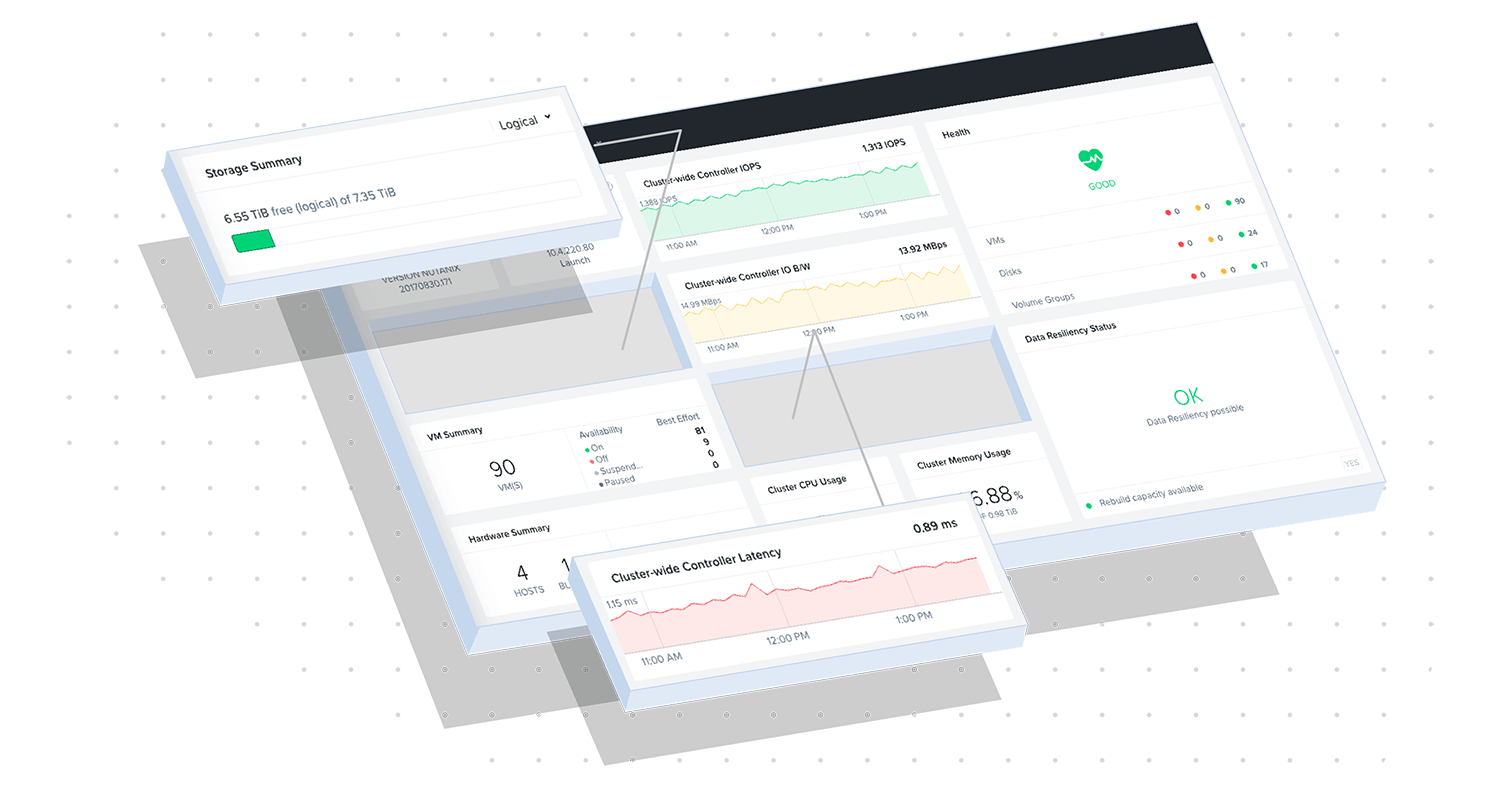
Nutanix Unified Storage is a software-defined storage platform that consolidates File, Object & Block storage into a single platform. By removing the need for dedicated storage systems, the environment is simpler to operate, allowing you to focus more on application services and less on infrastructure. Combined with Nutanix Cloud Platform, Unified Storage gives you a platform that is built for scale, performance, and integrated data security. It offers agility, flexibility and simplicity to build modern applications and services no matter where they are deployed - core, cloud, or edge. The platform provides seamless access to structured and unstructured data using S3, SMB, or NFS protocols. A single point of management for all storage resources eliminates complexity of multiple interfaces and consumer-grade design enables non-storage experts to handle most day-to-day storage and data management tasks. Data security and analytics integrated into the solution provide deep insights into how data is being used and helps to prevent threats from ransomware and other bad actors. With integrated ransomware protection, Unified Storage helps to detect, prevent, and recover from cyber-attacks.
Related articles:
Related Resources
2023 Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for distributed file systems and object storage

IDC white paper on the business value of Nutanix Unified Storage

Industry's First Unified Storage Platform for All Data Management Needs
Related products and solutions
Nutanix Unified Storage
Intelligently manage and share data to help your business make informed decisions.
Nutanix Files Storage
Centrally manage, scale and adapt to changing file-storage needs from on-premises to multiple clouds.
Nutanix Objects Storage
Objects Storage delivers secure S3-compatible object storage at massive scale to hybrid cloud environments.