Introducing AOS 6.6: Enhanced data services and simplified networking and security
By Allan Waters
The Nutanix team is excited to announce the availability of the AOS™ 6.6 software release, bringing even greater simplicity and efficiency to Nutanix® HCI deployments at organizations everywhere. AOS 6.6 builds on the innovations delivered in our last Long Term Support (LTS) release AOS 6.5 by providing efficiency updates around erasure coding and dedupe, delivering important updates around usability and enterprise readiness of infrastructure for business critical apps and a host of networking related features. Available today, AOS 6.6 ships with a new version of Prism Central, PC 2022.9, as well as the 8th generation of the Nutanix AHV® hypervisor, AHV 20220304.242.
The 8th Generation of AHV
Nutanix Cloud Infrastructure includes built-in virtualization powered by AHV. Built on an open-source foundation and extended with advanced enterprise features, AHV makes VM operations one-click simple for both traditional IT and modern cloud-native applications. AOS 6.6 includes the 8th generation of AHV, integrating updated upstream components of the open-source hypervisor core, as well as all-new VM operations capabilities. Upgraded ecosystem components include a new Linux® kernel as well as updated versions of the core hypervisor services. With an automated one-click hypervisor upgrade, Nutanix customers will benefit from enhanced performance and improved total cost of ownership without needing to upgrade licenses or hardware.
In addition to the inclusion of the latest open source components within the hypervisor core, several key optimizations specific to AHV improve both compute and storage performance, such as significantly improved context switching performance by removing key overheads in the switching path (on Intel® systems specifically). This helps response time on dense systems. We've also improved the effectiveness of idle polling by reducing spurious interruptions from Open vSwitch and other services, which applies to both AMD® and Intel systems. This is particularly impactful on very large and very dense systems (e.g. many dozens of cores, hundreds of VMs, like EUC/VDI) as well as workloads that are particularly latency sensitive (e.g. Epic®and SAP® workloads).
This release of AHV also includes several important security updates. First, AHV now supports Windows® 11 software with the introduction of the Virtual Trusted Platform Module (vTPM). vTPM is a virtualized software instance of the Trusted Platform Module (TPM), that carries out secure cryptographic operations to increase security against firmware attacks, and is a requirement for running Windows 11. Nutanix Guest Tools (NGT) has been updated to communicate with the CVM through a secure connection directly with AHV, without needing to establish an IP connection to the CVM.

VM Centric Data Policies
In AOS 6.1, Nutanix introduced VM centric storage policies to manage storage configs at per VM granularity across clusters. This is a huge improvement from traditional storage administration where policies are applied to a storage container and VMs are placed in the storage container that meets its requirements. Now administrators can create storage policies once in Prism Central and manage storage configs of VMs without manually creating storage containers for each cluster, and without needing to migrate VMs to other containers if requirements change. Storage policies are applied to VMs using categories in Prism Central.
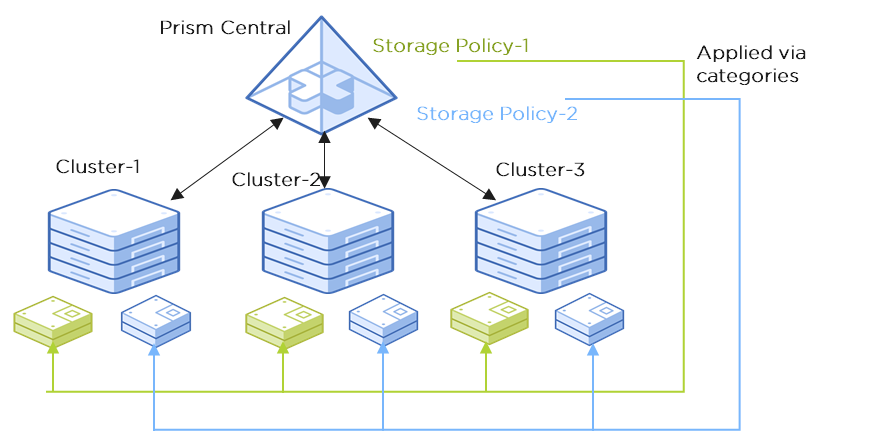
Figure 2. Storage Configuration with Storage policies
The first storage policies were introduced in AOS 6.1, giving administrators the ability to manage encryption, QoS and compression on a per-VM basis. AOS 6.6 enhances storage policy to support replication factor (RF) config which can also be applied at per VM granularity.
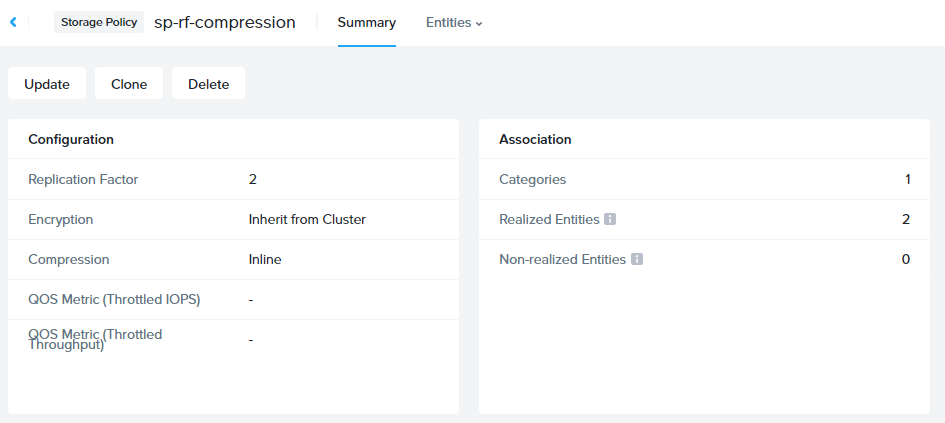
Additionally Prism Central 2022.9 provides administrators the ability to check policy compliance. VMs that are assigned storage policies are checked for compliance with the settings in that policy and reported in Prism Central. Compliance reporting gives administrators detailed feedback so they can take action to resolve the storage config of non-compliant VMs.
Simplified RDMA for Data Replication
AOS has long supported RDMA (Remote Direct Memory Access), and AOS 6.6 makes it even easier to set up and manage. RDMA improves latency by enabling direct data transfer between CVMs without the overhead of the TCP/IP stack, reducing latency and decreasing CPU utilization. With supported network hardware and a dedicated NIC, administrators can use RDMA for replication traffic between hosts. Before AOS 6.6, administrators had to set up RDMA during the foundation process, and required network switch configuration to use RDMA.
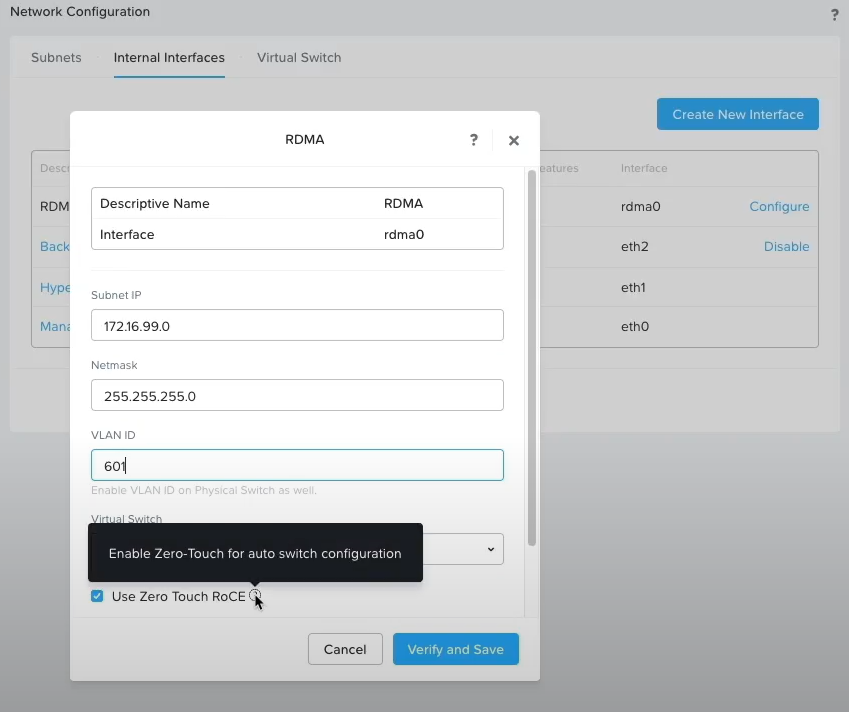
AOS 6.6 simplifies RDMA configuration in two significant ways. First, RDMA with ZTR (Zero Touch RoCE) makes it possible to utilize RDMA, without the need for administrators to configure switching infrastructure for priority flow control (PFC) or explicit congestion notification (ECN) or worry about switch compatibility. As long as network cards within the Nutanix hosts support ZTR, RDMA can be configured for data replication without changing switch configuration. Second, RDMA can now be configured on existing clusters through Prism, instead of needing to be configured via Foundation during cluster creation. These two new capabilities greatly lower the barrier to adoption of RDMA, making it possible for more customers to benefit from increased storage performance with reduced CPU utilization.
Data Efficiency
Nutanix AOS utilizes a multitude of data reduction techniques to minimize the amount of physical storage capacity needed to store application data within a cluster. AOS 6.6 brings significant enhancements to two of them: Deduplication and Erasure Coding.
Sub-Extent Deduplication
Deduplication increases available storage capacity by detecting duplicate chunks of data and only storing a single copy to physical media. This is particularly effective for data sets that store multiple copies of the same data, or when multiple VMs are separately storing the same underlying data. AOS 6.6 improves efficiency by deduplicating at a sub extent level rather than the entire 1MB extent, increasing the chances of detecting duplicate blocks and reducing the amount of metadata needed to track the deduplicated segments. The result is better space savings for the same dataset without incurring a greater metadata overhead.
Inline Erasure Coding for Nutanix Objects
AOS 6.6 also introduces inline erasure coding for Nutanix Objects, enabling greater density for data that is typically only written once and never updated, such as for backup and archiving. AOS has long supported post-process erasure coding, where data is protected through parity calculations instead of replication. Erasure coding is similar to traditional RAID conceptually, except the data and parity calculation are distributed across separate server nodes instead of across local storage drives. Recalculating parity when data is updated requires cluster resources, so historically only data that has been detected as “write-cold” would be erasure coded. Because Nutanix Objects data is only written once, it can be erasure coded at ingest, optimizing both storage capacity and compute resources.

Figure 3. Erasure Coding via www.nutanixbible.com
Networking
Networking functionality has also been enhanced in several critical ways, simplifying management at scale and enabling multi-tenant network administration, as well as expanding the capabilities of VPCs within Flow Virtual Networking. Network admins will also appreciate SPAN enhancements that make it possible to capture traffic at a VM in addition to the existing physical NIC capture functionality.
AOS 6.6 also introduces several new features for Early Access, including the new v4 APIs for networking as well IPFix export APIs.
Networking RBAC
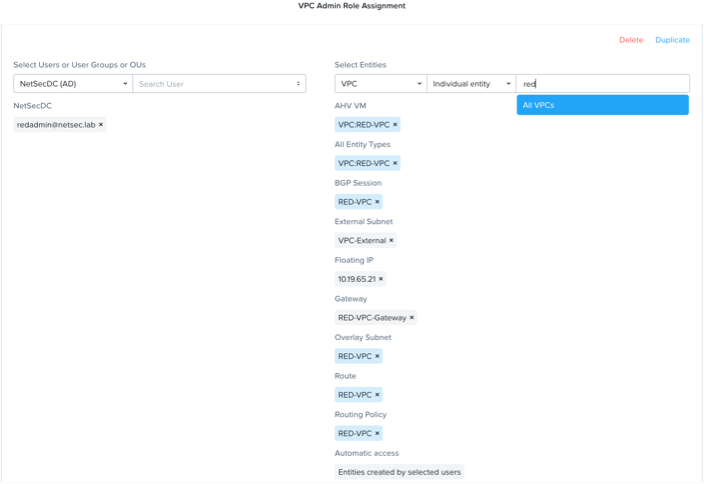
Role based access control has been extended to include networking capabilities, allowing administrators to delegate least privileged administrative access to network entities such as VPCs, Subnets, Routes, Policies, and more. The combination of defined roles and entity filters, along with projects, makes it possible for the Nutanix platform to deliver a multi-tenant networking and network administration experience.
VPC BGP Gateway
Flow Virtual Networking gets a new dynamic integration point thanks to the BGP function of the Network Gateway VM. Now VPCs can dynamically advertise their externally routable prefix to the upstream network, simplifying configuration burden and enabling new use cases like network mobility. Now, the location of the VPC as well as the VPC itself are both software defined. Administrators can combine this BGP advertisement with priorities to make networks that seamlessly migrate from site to site during disaster scenarios or maintenance.
VPC Migration
For existing environments it’s now easier than ever to move VMs from traditional VLAN backed networks to VPC subnets. A new Prism Central wizard allows you to select groups of Nutanix VMs to migrate from VLAN subnets to VPC subnets with built-in planning and tracking capabilities, all while maintaining VM MAC addresses. This makes it even easier to utilize VPCs to manage Nutanix environments at scale.
For non-Nutanix VMs, Move now supports Nutanix VPC subnets as a destination, so regardless of where your VMs are coming from, we make it easy to migrate them to a Nutanix VPC.
Security
As cybersecurity grabs further mindshare of the IT landscape, Prism Central continues to build on turn-key protection, detection, and remediation measures for you to use. Version 2022.9 introduces a holistic platform security dashboard to better manage the security posture of your Nutanix infrastructure. Paired with Security Central for your workloads, and Data Lens for your data, you can now quickly achieve total operational security responsiveness.
Platform Security Dashboard
The multicloud nature of Nutanix requires detailed but instant feedback of critical security insights throughout all your Nutanix clusters. The new Prism Central Platform Security Dashboard creates a single overview for IT administrative staff of Nutanix solutions of the overall security state of the system focused on three key areas:
- Security Hardening:
Understand and highlight Nutanix platform security controls in one simple view with fast access to change these directly in Prism Central. - CVE Management:
Quickly assess and mitigate risks and exposures of infrastructure CVEs ( Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures) using one-click integration with LCM (life-cycle management) for remediation. - STIG Management:
Monitor and report compliance to STIGs (Security Technical Implementation Guides).
Disaster Recovery
In addition to protecting your applications and data against hardware failure, AOS includes extensive support to protect against disaster as well. AOS 6.6 extends this functionality with network segmentation for DR workloads, simplified management, and support for even tighter RPOs.
Network Segmentation for DR
For existing and new deployments, we have added support for Network Segmentation for Policy Based in Prism Central. This feature allows for replication traffic to be either logically segmented (VLAN based) over the existing network interfaces or physically segmented on to separate network interfaces and virtual switch. This not only allows for flexibility in securing DR replication traffic, it also reduces bandwidth contention when using physical segmentation. This feature rounds out the ability to segment all DR related traffic whether you use Protection Domains or Policy Based Disaster Recovery in Prism Central
Policy Based Volume Group and Consistency Group Replication
In AOS 6.6 we have added the capability to manage the protection, replication and failover for both volume groups and consistency groups all within Prism Central. This is a huge step in continuing to move our replication management to Prism Central and will provide a more unified management experience for our customers.

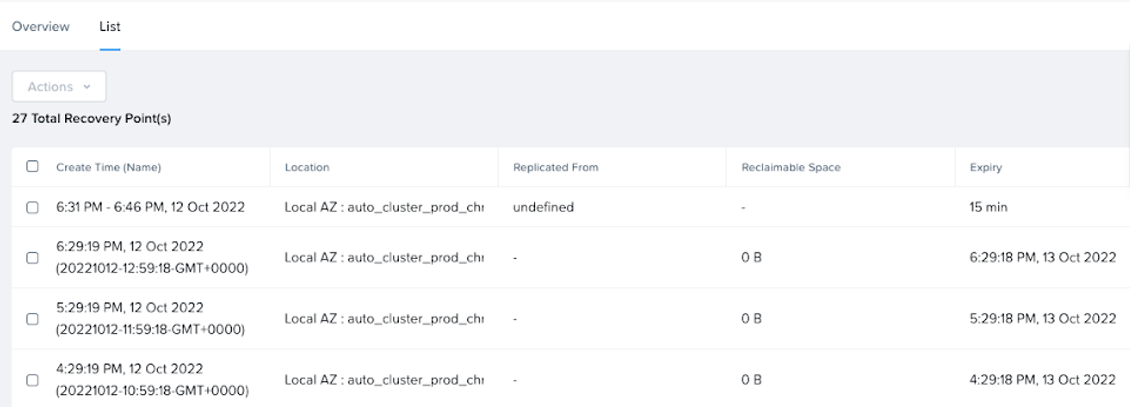
NearSync Enhancements
Also in AOS 6.6 and PC 2022.9 we have added support for 20 second RPO utilizing our NearSync replication in both Protection Domain and Policy Based workflows. The screenshots below show a VM protected with NearSync will have hourly recovery points (roll ups) as well as the ability to restore anywhere within the last 15 minutes of NearSync snapshots.

Early Access to Version 4 API Enhancements for Developers
This release brings exciting updates for partners, developers, and automation fans to the version 4 (v4) Early Access Nutanix REST APIs. To learn more about how these features make your development and automation work easier with multi-language SDKs, easy-to-follow examples, and more visit Nutanix.dev.
Examples of enhancements include:
- VM and VM template management and operations.
- Cluster management - Expand cluster and remove node from an existing cluster, and configure (CRUD operations) cluster properties, SNMP and Remote Syslog server.
- Networking - Manage networking configuration including advanced networking operations on Nutanix clusters.
- Security Dashboard
Upgrade Today
Take advantage of these latest enhancements, in addition to bug fixes and patches, by upgrading to AOS 6.6 today. For more details on these features and compatibility, read the release notes and to get started download the binaries from the support portal.
Learn more about the previous AOS 6.5 LTS release here
Read the Top 10 Reasons Why Nutanix
© 2022 Nutanix, Inc. All rights reserved. Nutanix, the Nutanix logo and all Nutanix product, feature and service names mentioned herein are registered trademarks or trademarks of Nutanix, Inc. in the United States and other countries. Other brand names mentioned herein are for identification purposes only and may be the trademarks of their respective holder(s). This post may contain links to external websites that are not part of Nutanix.com. Nutanix does not control these sites and disclaims all responsibility for the content or accuracy of any external site. Our decision to link to an external site should not be considered an endorsement of any content on such a site. Certain information contained in this post may relate to or be based on studies, publications, surveys and other data obtained from third-party sources and our own internal estimates and research. While we believe these third-party studies, publications, surveys and other data are reliable as of the date of this post, they have not independently verified, and we make no representation as to the adequacy, fairness, accuracy, or completeness of any information obtained from third-party sources.